Sleep apnea affects millions worldwide, and choosing the right treatment can significantly impact your quality of life. However, understanding the differences between CPAP and Auto CPAP machines often confuses patients and caregivers alike.
This comprehensive guide examines both therapies, helping you make an informed decision about your sleep apnea treatment. Moreover, we'll explore clinical evidence, costs, and practical considerations for each option.
Understanding Sleep Apnea and PAP Therapy
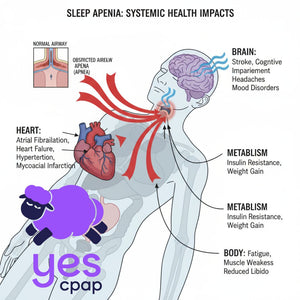
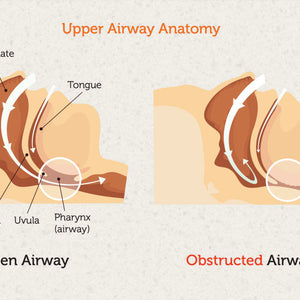
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) occurs when throat muscles relax during sleep, causing airway collapse. Subsequently, this leads to breathing interruptions that can happen hundreds of times per night.
Positive Airway Pressure (PAP) therapy works as a pneumatic splint. Therefore, it delivers pressurized air through a mask to keep your airway open throughout the night.
What is CPAP Therapy?
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) delivers a single, fixed pressure level throughout your entire sleep period. Furthermore, this pressure setting comes from a sleep study called titration.
How CPAP Works
During titration, sleep technologists monitor your breathing patterns and systematically increase pressure. Consequently, they identify the exact pressure needed to eliminate all breathing events. Additionally, this setting accounts for your worst-case scenarios, including REM sleep and back-sleeping positions.
Key CPAP Features
Modern CPAP machines include several comfort features:
- Ramp function: Gradually increases pressure over 5-45 minutes
- Heated humidification: Prevents dryness and nasal congestion
- Expiratory pressure relief: Reduces pressure during exhalation for comfort
What is Auto CPAP (APAP)?
Auto-adjusting Positive Airway Pressure (APAP) uses sophisticated algorithms to monitor your breathing continuously. As a result, it automatically adjusts pressure based on real-time needs within a prescribed range.
How Auto CPAP Works
APAP machines analyze airflow patterns breath-by-breath, detecting signs of airway obstruction. Therefore, when the device senses snoring or flow limitations, it increases pressure immediately. Conversely, when breathing stabilizes, the machine reduces pressure to the minimum effective level.
Advanced APAP Technology
APAP algorithms respond to various breathing events:
- Flow limitations and snoring
- Hypopnea events (partial airway blockages)
- Complete apnea episodes
- Changes in sleep position or stages
Clinical Evidence: CPAP vs Auto CPAP Effectiveness
Multiple studies demonstrate therapeutic equivalence between CPAP and APAP for treating OSA. However, subtle differences exist in secondary outcomes and patient experience.
Primary Treatment Outcomes
Research consistently shows both therapies achieve similar results:
- AHI Reduction: No clinically significant difference (0.25 events/hour variance)
- Oxygen Saturation: CPAP shows slight advantage (+1.3% minimum saturation)
- Sleep Quality: Both effectively restore normal sleep architecture
Patient Adherence Comparison
APAP shows marginal advantages in compliance:
- Usage Time: 11 minutes more per night on average
- Comfort Ratings: Lower average pressure improves tolerance
- Adaptation Period: Easier initial adjustment for new users
Nevertheless, these differences are statistically significant but clinically marginal according to sleep medicine experts.
When to Choose CPAP
CPAP remains the gold standard for many patients. Therefore, consider CPAP if you have:
Ideal CPAP Candidates
- Consistent OSA patterns: Stable breathing events regardless of sleep position
- Pressure sensitivity: Some patients find APAP pressure changes disruptive
- Cost considerations: CPAP costs 20-30% less than APAP machines
- Cardiovascular comorbidities: Fixed pressure may offer better blood pressure control
CPAP Advantages
- Extensively researched with decades of clinical data
- Simple, reliable "set-and-forget" operation
- Lower purchase and maintenance costs
- Proven effectiveness across all OSA severity levels
When to Choose Auto CPAP
APAP excels in managing variable sleep apnea patterns. Furthermore, it adapts automatically to changing conditions without manual adjustments.
Ideal APAP Candidates
- Positional sleep apnea: Worse breathing when sleeping on your back
- REM-related OSA: Increased events during dream sleep
- Variable nightly needs: Affected by allergies, congestion, or alcohol consumption
- Weight fluctuations: Pressure needs change with weight loss or gain
APAP Advantages
- Delivers minimum effective pressure for optimal comfort
- Eliminates need for repeat sleep studies after weight changes
- Enables home titration, reducing healthcare costs
- Automatically adapts to temporary conditions like colds
Cost Comparison and Insurance Coverage
Understanding the financial implications helps you plan for long-term therapy success.
Side Effects and Troubleshooting
Both therapies share common side effects, but management strategies differ slightly.
Common Side Effects
- Nasal dryness and congestion
- Mask leaks and discomfort
- Aerophagia (air swallowing)
- Claustrophobia or anxiety
CPAP-Specific Considerations
Fixed pressure can feel overwhelming initially. Therefore, use ramp features and consider expiratory pressure relief for comfort.
APAP-Specific Considerations
Pressure fluctuations may disturb light sleepers. However, most patients adapt within 2-4 weeks of consistent use.
Expert Recommendations from Sleep Medicine
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine provides clear guidance on therapy selection:
Strong Recommendations
- Both CPAP and APAP are equivalent first-line treatments for OSA
- Home APAP titration equals in-lab CPAP titration for most patients
- Patient preference should guide therapy selection when both options are suitable
Contraindications for APAP
- Central sleep apnea or complex sleep apnea
- Significant heart failure with Cheyne-Stokes breathing
- Severe COPD or obesity hypoventilation syndrome
Making Your Decision: Key Factors
Consider these factors when choosing between CPAP and APAP:
Choose CPAP If:
- Budget constraints are primary concerns
- You prefer simple, predictable therapy
- Sleep patterns remain consistent nightly
- Previous APAP experience caused sleep disruption
Choose APAP If:
- Comfort and adaptability are priorities
- You have positional or REM-related sleep apnea
- Weight management is ongoing
- Home titration appeals to you
Future of Sleep Apnea Technology
Both CPAP and APAP devices now incorporate advanced monitoring capabilities. Therefore, modern machines transmit detailed usage data to healthcare providers through cellular connections.
This telemonitoring revolution enables:
- Proactive problem identification
- Remote troubleshooting support
- Personalized therapy adjustments
- Improved long-term adherence rates
Conclusion
CPAP and Auto CPAP both effectively treat obstructive sleep apnea with equivalent clinical outcomes. However, the choice depends on your specific needs, comfort preferences, and financial considerations.
Furthermore, successful PAP therapy requires consistent usage regardless of device type. Therefore, prioritize the option that feels most comfortable and sustainable for your lifestyle.
Finally, consult with a qualified sleep specialist to determine which therapy aligns best with your clinical profile. Additionally, remember that the most effective therapy is the one you'll use consistently every night.
This article provides educational information and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making treatment decisions.
References
Clinical and Research Sources
-
Sullivan, C. E., et al. (1981). Reversal of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea by Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Applied Through the Nares. The Lancet, 317(8225), 862-865.
-
American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2019). Clinical Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring with Oral Appliance Therapy: An Update for 2015. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.
-
Comparative Meta-Analysis Studies (2016-2024). CPAP vs APAP Efficacy in OSA Treatment: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep Medicine Reviews.
-
Herikurniawan, J. A., & Adelya, F. (2024). Ventilasi Noninvasif pada Obstructive Sleep Apnea dan Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome. Jurnal Penyakit Dalam Indonesia, 11(3), 178–185.
Singapore Market and Product Sources
-
YesCPAP Singapore. (2025). Resvent iBreeze Auto CPAP Series - Product Specifications and Pricing. https://yescpap.com/collections/all
-
YesCPAP Singapore. (2025). CPAP Singapore Professional Sleep Apnea Solutions. https://yescpap.com/blogs/news/cpap-singapore-professional-sleep-apnea-solutions-by-yescpap
-
YesCPAP Singapore. (2025). Mastering CPAP Therapy: First Night Guide. https://yescpap.com/blogs/news/mastering-cpap-therapy-first-night-guide
-
YesCPAP Singapore. (2025). CPAP Troubleshooting Guide: Common Side Effects. https://yescpap.com/blogs/news/cpap-troubleshooting-guide-common-side-effects
Singapore Healthcare and Regulatory Sources
-
Health Sciences Authority (HSA) Singapore. Medical Device Registration - CPAP Devices (DE0507383).
-
Ministry of Health Singapore (2024). MediShield Life Coverage Guidelines and Exclusions.
-
Central Provident Fund (CPF) Singapore (2024). MediSave Usage Guidelines for Medical Equipment.
International Sleep Medicine Guidelines
-
Sleep Foundation. (2025). APAP vs CPAP Treatment Comparison. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/cpap/apap-vs-cpap
-
ResMed International. (2025). APAP vs CPAP: Sleep Apnea Treatments Explained. https://www.resmed.com/en-us/sleep-health/blog/what-is-apap-and-how-is-it-different-than-cpap/
Note: All clinical information in this article is based on peer-reviewed research and official medical guidelines applicable to Singapore's medical practice standards. Product pricing reflects current YesCPAP.com rates as of 2025 with promotional discounts applied. Always consult qualified sleep specialists at Singapore General Hospital, National University Hospital, or other accredited sleep centers for personalized medical advice.