Educational Content by YesCPAP Team
For informational purposes only - Always consult healthcare professionals
Last Updated: September 2025
What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea happens when your breathing stops and starts repeatedly during sleep. The word "apnea" comes from Greek, meaning "without breath." While this might sound scary, understanding the signs can help you take the right steps.
Many people live with sleep apnea without knowing it. However, recognizing the symptoms early makes a big difference for your health and quality of life.
Common Signs to Watch For
During Sleep
Loud, Irregular Snoring Not all snoring means sleep apnea, but certain patterns deserve attention. Instead of steady snoring, you might notice:
- Snoring that stops suddenly, then resumes with gasping
- Very loud snoring that wakes others
- Snoring that happens in all sleeping positions
Breathing Interruptions Partners often notice these first. You might see someone:
- Stop breathing for several seconds
- Gasp or choke during sleep
- Toss and turn frequently
- Sweat heavily at night
During the Day
Persistent Tiredness Even after a full night's sleep, you might feel:
- Exhausted throughout the day
- Difficulty staying awake during quiet activities
- Need for frequent naps
- Difficulty concentrating at work or school
Other Daytime Signs
- Morning headaches that fade after a few hours
- Dry mouth or sore throat upon waking
- Mood changes or irritability
- Memory problems
Different Presentations
In Children
Children with sleep apnea often show different signs:
- Bedwetting after being toilet-trained
- Hyperactivity or attention problems
- Poor school performance
- Unusual sleeping positions
- Heavy sweating during sleep
In Women
Women may experience:
- Insomnia or restless sleep
- Morning headaches
- Mood changes
- Less obvious snoring
- Fatigue that's often attributed to other causes
In Older Adults
Sleep apnea in seniors can be confused with normal aging:
- Increased confusion or memory issues
- Falls due to daytime sleepiness
- Worsening of other health conditions
- Changes in medication effectiveness
Understanding the Types
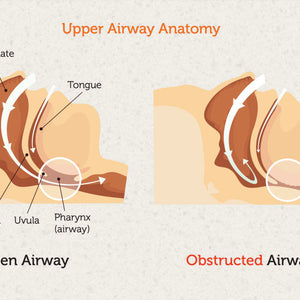
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (Most Common) The throat muscles relax too much, blocking the airway. This creates the classic stopping-and-starting breathing pattern.
Central Sleep Apnea (Less Common) The brain doesn't send proper signals to breathing muscles. This type often relates to other medical conditions.
Complex Sleep Apnea A combination of both types, which requires specialized treatment approaches.
When to Seek Help
Consider talking to a doctor if you notice:
- Regular snoring with breathing interruptions
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Morning headaches several times per week
- Difficulty concentrating at work or school
- Partner complaints about your sleep patterns
Lifestyle Factors That May Help
While medical treatment is often necessary, certain lifestyle changes can support better sleep:
Sleep Position
- Try sleeping on your side instead of your back
- Use pillows to maintain side-sleeping position
- Elevate your head slightly
Healthy Habits
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule
- Avoid alcohol before bedtime
- Keep your bedroom cool and dark
- Exercise regularly, but not close to bedtime
Weight Management
- Even small weight losses can make a difference
- Focus on sustainable, healthy eating habits
- Consider working with healthcare professionals
Treatment Approaches
CPAP Therapy
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines are commonly prescribed for moderate to severe sleep apnea. These devices:
- Provide steady air pressure to keep airways open
- Come in various sizes and comfort features
- Require some adjustment time but can be very effective
- Include humidification options for comfort
Other Options
- Oral appliances for mild cases
- Surgical procedures in specific situations
- Combination approaches based on individual needs
- Lifestyle modifications as supporting measures
Living Well with Treatment
Getting Started
- Work closely with your healthcare team
- Be patient during the adjustment period
- Ask questions about your treatment options
- Connect with support groups if helpful
Long-term Success
- Regular follow-ups help optimize treatment
- Equipment maintenance keeps therapy effective
- Lifestyle habits support overall health
- Most people feel significantly better with proper treatment
Supporting Family Members
If someone in your family might have sleep apnea:
- Gently share your observations
- Offer to accompany them to medical appointments
- Be patient during treatment adjustment
- Learn about their treatment to provide support
Sleep Hygiene for Everyone
Good sleep habits benefit the whole family:
- Keep consistent bedtimes and wake times
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine
- Limit screen time before sleep
- Make bedrooms comfortable for rest
- Address stress and anxiety that affects sleep
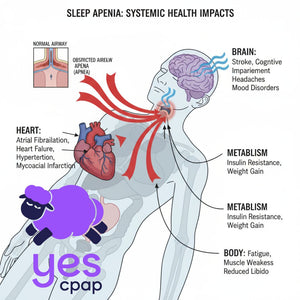
Important Health Connections
Sleep apnea can affect other aspects of health:
- Blood pressure and heart health
- Blood sugar control
- Mental health and mood
- Memory and concentration
- Accident risk due to sleepiness
However, proper treatment often leads to improvements in these areas over time.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
About Symptoms:
- Are my symptoms consistent with sleep apnea?
- What type of sleep study might be helpful?
- How urgent is evaluation and treatment?
About Treatment:
- What treatment options suit my situation?
- How long does adjustment to treatment typically take?
- What improvements can I expect and when?
- How will we monitor treatment effectiveness?
Available Support in Singapore
Healthcare System
- Public hospitals offer sleep disorder clinics
- Private specialists provide comprehensive care
- Sleep studies can be arranged through referrals
- Insurance coverage varies by plan and provider
Equipment and Support
- Medical equipment providers offer various options
- Training and support help with treatment adjustment
- Maintenance services keep equipment working properly
- Replacement parts and supplies are readily available
Moving Forward
Sleep apnea is a common condition that affects many people. The important thing is recognizing potential signs and taking appropriate action. With proper medical evaluation and treatment, most people experience significant improvements in their sleep quality and overall health.
Remember that everyone's situation is unique. Therefore, working with healthcare professionals ensures you receive the most appropriate care for your specific needs.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep apnea involves repeated breathing interruptions during sleep
- Signs include loud snoring, observed breathing stops, and daytime tiredness
- Different age groups and genders may show varying symptoms
- Medical evaluation can determine if treatment is needed
- Various treatment options are available and often very effective
- Lifestyle changes can support medical treatment
- Most people feel much better with appropriate care
Important Note: This guide provides general educational information only. It does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult qualified healthcare providers for personalized medical guidance.
About This Guide: Created to help Singapore families understand sleep apnea symptoms and treatment options. For specific medical questions or treatment decisions, please consult with qualified healthcare professionals who can evaluate your individual situation.